Athlete’s foot also known as tinea pedis, is a fungal infection on the skin of the foot. It is characterized by itchy, moist, white, scaly lesions between the toes that can spread to the sole of the foot. Athlete’s foot is contagious and spreads through contact with infected skin scales or fungi in moist areas such as swimming pools and bathrooms, or from sharing shoes of an infected person or having contact with pets carrying the fungi. It is a chronic infection that can recur after treatment.
A common symptom of athlete’s foot is moist, itchy, scaly lesions between the toes; another form presents as dry, peeling skin between the toes. The area often becomes red and itchy. You may also feel a burning sensation between your toes. If the infection spreads to your toenails, they can become thick and discolored.
Treatment
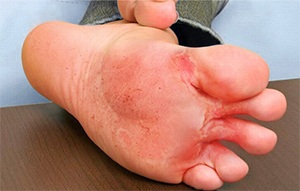
Treatment of athlete’s foot includes antifungal skin creams or oral medicines containing miconazole, clotrimazole, or tolnafate. The skin creams should be applied to the affected area in small amounts at least once a day. You should continue applying the cream daily for 1 – 2 weeks, even after the infection clears from your feet to prevent the infection from recurring. A medicated powder may also be given to help keep the feet dry. The fungal infection can last three to four weeks.
Preventive Tips
- Wash your feet every day with soap and water
- Keep your feet clean and dry, preferably between your toes
- Keep your nails short and clean because nails can house the fungi and spread the infection
- Wear clean socks made of cotton, and change them often in order to keep your feet dry
- Avoid walking barefoot in public areas. Wear proper shoes that support good air circulation to your feet





